Operating systems have slightly different signing procedures, but conceptually they are the same. Apps that are distributed for use by others must be signed. Even though ArcGIS AppStudio will perform the app signing and build process for you, you must still obtain signing files from each operating system vendor to supply as inputs to AppStudio.
The complete edition of the NSB/AppStudio development environment contains everything you need to create apps and download them to your mobile device. Reference documentation, samples and tutorials are also included. Download AppStudio here: Mac - or - Windows.
- ArcGIS AppStudio is a groundbreaking tool in the GIS app revolution. With AppStudio, you can convert your maps into beautiful, consumer-friendly mobile apps that are ready for Mac, iOS, Android, Windows, and Ubuntu operating systems and publish them to all the popular app stores using your own brand—no developer skills required.
- AppStudio is a powerful development environment that lets you build apps on your desktop machine, then run it on your device of choice. With AppStudio, you’ll be able to program your applications in JavaScript or BASIC using your Windows or Mac desktop, then port your creations over to iOS and Android devices quickly and easily.
Prepare a new app
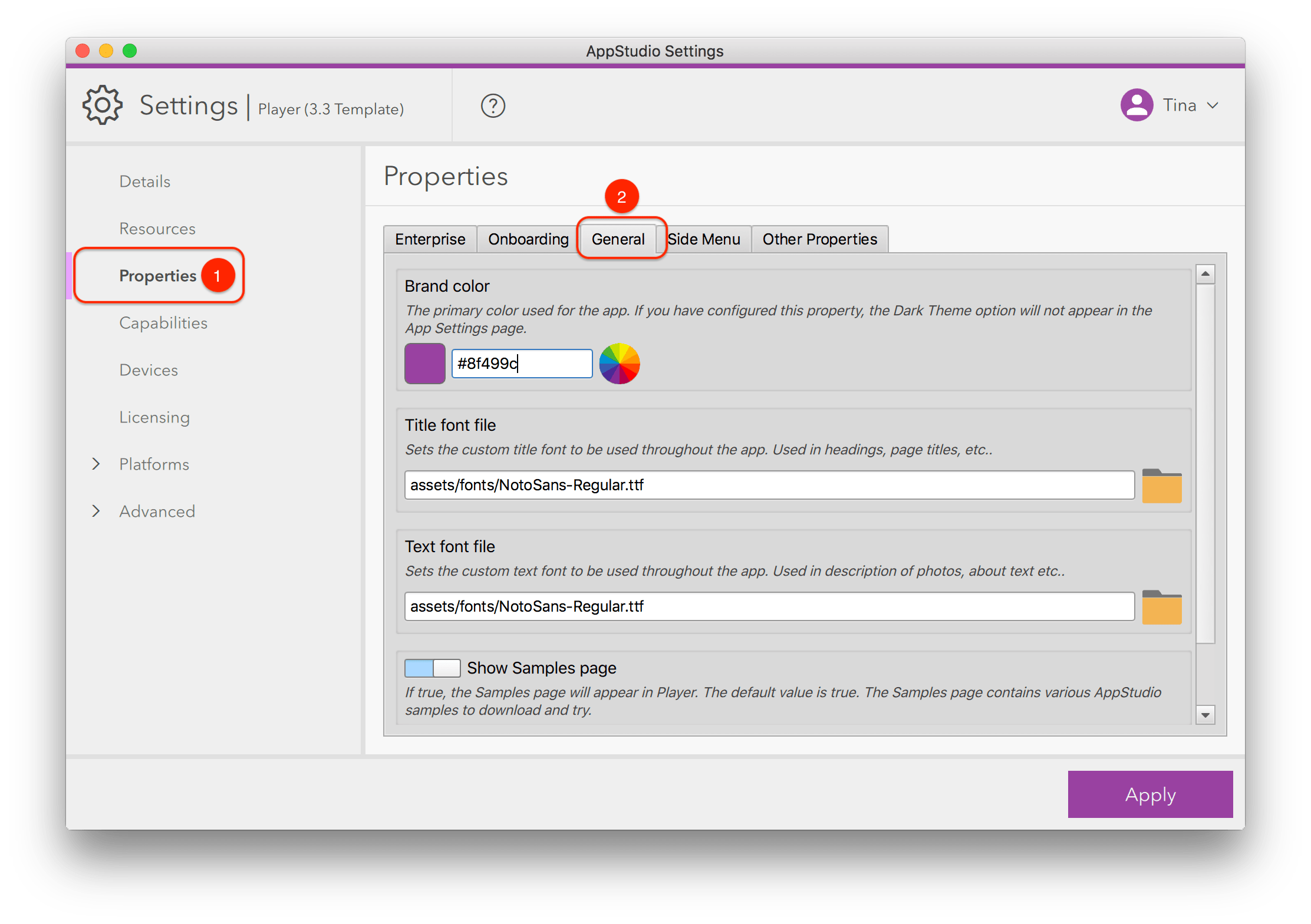
Before you sign and release your app, it should be given an ArcGIS Client ID, a redirect URI, and a license string. While an app can still be built without a Client ID or redirect URI, both are important in an app using ArcGIS services.
An ArcGIS Client ID—also called the AppID—is needed for named user sign-in for all apps. To obtain a Client ID, go to https://developers.arcgis.com, sign in with your developer credentials, click the drop-down arrow next to Dashboard, and choose New Application. Once registered, you'll receive a Client ID, which you can copy into your AppStudio app. If you're using ArcGIS AppStudio, a Client ID can also be generated in Settings > Licensing by clicking the Register button.
If your app requires named user sign-in, you also need to provide a redirect URI. Redirect URIs represent valid places that a user can be redirected to after completing an OAuth sign-in. To add a new redirect URI for your app, go to the Authentication tab for your application on https://developers.arcgis.com. Here, register your app if you haven't already, and add your own redirect URI, or add urn:ietf:wg:oauth:2.0:oob to use the hosted redirect page back to your app on ArcGIS Online. The urn:ietf:wg:oauth:2.0:oob URI is also automatically set for any apps made and registered in ArcGIS AppStudio.
A license string is required to build apps that use the ArcGIS Runtime version 100.x. An app cannot be built without a license string, which also denotes the functions of the ArcGIS platform that the app is authorized to perform. For information on how to obtain a license string, see License your app.
Sign your iOS app
All iOS apps need to be signed. Apps created for testing must be signed by a developer certificate that is tied to your Apple developer account and the device on which you do your testing. A production certificate is tied only to your Apple developer account.
Before running the Make tool found in the AppStudio gallery side panel, either cloud or local, ensure that you have provided the following in the iOS tab of Settings, found under the Platforms heading:
- Bundle ID—Always use a reverse internet domain name, for example, com.companyname.applicationname. The package name is a unique identifier for the app and is the default name for the application process. Once you publish your app, you cannot change the package name. For additional details, see the bundle ID explanation in Prepare for app distribution.
- Provisioning profile—Indicates the devices where you plan to run your app.
- Certificate (.p12 file)—Certificate for either the App Store or in-house distribution. This file is created in Keychain Access. If you do not supply both this information and the bundle ID in AppStudio, installation files will not be generated. For more information, see What is app signing?
At the time of running the Make tool, you will be prompted to supply the certificate password. Farming simulator for mac.
To create the certificate file required for signing, the following steps need to be performed once per developer and require a Mac:
- Download your developer certificate (for example, ios_developer.cer) from the iOS Dev Center.
- Download your mobile provisioning profile (for example, ios_developer.mobileprovision) from the iOS Dev Center.
- Use Finder to browse to Applications > Utilities > Keychain Access.
- Import your certificate into Keychain Access.
- In Keychain Access, from the Keychain list, choose login, and from the Category list, choose My Certificates. Choose the certificate named phone Developer: Your Name and export the certificate with the private key with a password (for example, john_doe_private_key.p12).
- In AppStudio, browse to Settings > Platforms > iOS.
- Set the provisioning profile path.
- Set the distribution type for your app. For more information on the options, see the Xcode documentation on distribution methods.
Note:
Double-click the .p12 certificate file and mobile provisioning profile to import the files.
If you're using AppStudio on macOS, two additional properties must be set for building iOS apps with local Make. The contents of these fields can be found in your development or distribution certificate, which can be seen using Finder to browse to Applications > Utilities > Keychain Access.
Provide the certificate's organizational unit in the Team ID field.

Provide the certificate's common name in the Code Signing Identity field.
Sign your Android app
To prepare an Android release build, you must first generate a signing keystore file. For detailed information on how to create this file, see the Android documentation.
Before running the Make tool, either cloud or local, ensure that you have provided the following in the Android tab of Settings, found under the Platforms heading:
- Package name—Always use a reverse internet domain name, for example, com.companyname.applicationname. The package name is a unique identifier for the app and is the default name for the application process. Once you publish your app, you cannot change the package name. For additional details, see the package name explanation in the manifest element of the Android SDK.
- Keystore file path—The location of the keystore file on your desktop machine.
- Key alias—Key name created at the time of keystore creation.
If you do not supply this information, your installation files will still be created, but they will be unsigned. Unsigned files can be installed for testing purposes but cannot be submitted to the Google Play Store or Amazon Appstore.
At the time of running the Make tool, you will be prompted to supply the keystore and key passwords.
To create a keystore, the following steps need to be performed once per developer:
- Download and install the Java Development Kit (JDK) from http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html.
- Create an environment variable named JAVA_HOME on your desktop machine: http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19182-01/820-7851/inst_cli_jdk_javahome_t/index.html.
- Add the JDK bin folder path to your PATH environment variable.
- In a command window, use the following to create the key: keytool -genkey -v -keystore [keystore_name].keystore -alias [alias_name] -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -validity 10000, where keystore_name is the name you choose for the resultant keystore file, and alias_name is the name you choose as an alias.
- Enter a keystore password and confirm.
- Enter additional information and confirm.
- Enter a key password. This password can be unique, or press Enter to use the same password as the keystore password.
Your keystore file will be created in the folder where you ran this command.
Sign your Mac app
Similar to Android, if you do not supply a certificate when you request Mac installation files, they will still be created, but they will be unsigned. Unsigned files can be installed for testing purposes but cannot be submitted to the Mac Store. The following steps are similar to iOS; however, a provisioning profile is not required for Mac.
See the maintaining certificates section of the App Distribution Guide to learn more about distribution signing identities.
Before running the Make tool, either cloud or local, ensure that you have provided the following in the macOS tab of Settings, found under the Platforms heading:
- Bundle ID—Always use a reverse internet domain name, for example, com.companyname.applicationname. The package name is a unique identifier for the app and is the default name for the application process. Once you publish your app, you cannot change the package name. For additional details, see the bundle ID explanation in Prepare for app distribution.
- Certificate (.p12 file)—Certificate for either the App Store or in-house distribution. This file is created in Keychain Access. If you do not supply both this information and the bundle ID in AppStudio, installation files will not be generated. For more informaiton, see What is app signing?
At the time of running the Make tool, you'll be prompted to supply the certificate password.
To create the certificate file required for signing a Mac app, follow the same steps as described above for iOS apps.
Sign your Universal Windows Platform app
To build Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps, you need to provide a publisher ID for your app.
Before running the Make tool, either cloud or local, ensure that you have provided the following in the Universal Windows Platform tab of Settings, found under the Platforms heading:
- Package name—A case-sensitive string between 3 and 50 characters in length consisting only of alphanumeric characters, periods and dashes. This is different from the name of your app that users will see. For additional details, see the Name attribute in the Identity page of Microsoft's developer documentation.
- Product ID—A GUID used to identify your app. When you make an update to your app, this GUID will ensure that the update matches the previous app. This is automatically generated without your input, but can be modified or regenerated if needed.
- Publisher ID—A string that fits the regular expression of a distinguished name. If you're providing a certificate, this publisher ID must match the publisher subject information provided in the certificate. For additional details, see the Publisher attribute in the Identity page of Microsoft's developer documentation.
- Certificate (.p12 or .pfx file)—Certificate for either the Windows Store or in-house distribution. See Create a certificate for package signing in Microsoft's developer documentation for more information.
Node.is
Node Package Manager
Electron
Introduction
AppStudio now supports the use of some of the most important new technologies in the web development world.
Node.js is a runtime environment that executes JavaScript code outside the browser. That makes it suitable for writing server side software, which would normally be done in PHP or other languages. It works by having an executable stub which is able to call the V8 JavaScript engine, which powers Chrome.
npm is a repository of code which can be used with Node.js. It's included when you download Node. There is a huge number of packages available - over 750,000 at last count. You can include these packages in your Node project to add functionality. It might be for convenience: there are a lot of libraries which are much easier to include in your project than to write yourself. It might be for functionality: the modules can implement features which would not be available in the browser.
An example of a convenient library would be Lodash which adds hundreds of additional functions to JavaScript. A missing feature library would be fs-extra which allows full access to the file system.
Electron is framework which allows for the development of desktop GUI applications. Since it's built on Node.js, it already has the ability to run JavaScript code. It also uses Chrome's browser engine to render the UI using regular HTML. Each Electron app includes the V8 Runtime as well as the Chrome browser. Slack, Github Desktop and WhatsApp are examples of apps built using Electron.

How is this compare to PhoneGap?
PhoneGap (Cordova) is used to package apps for iOS and Android. Electron is used to package apps for Windows, MacOS and Linux. It's quite reasonable to have one AppStudio project that you use with both PhoneGap and Electron, letting you build for all 5 platforms.
Nodejs/npm modules are similar to PhoneGap Plugins. Since they are operating system specific, PhoneGap Plugins will not work with Electron (and vice versa).
Tutorial: Make an Electron app
AppStudio allows you to make normal AppStudio apps (programmed in Javascript or BASIC) into full blown Electron apps. You can distribute these apps as regular executables, able to run on Windows, MacOS and Linux.
In this tutorial, we're going to use a module from npm called weather-js to create an app which gets weather data from weather.service.msn.com. It's very convenient: we don't have to figure out the MSN API to use it.
We recommend using AppStudio 8 (or later) with this tutorial.
Set up the project
1. Download and install Node. (This also installs npm.)
C# For Mac
2. Using AppStudio, create a new project called ElectronWeather and save it. (You can also use the ElectronWeather sample with comes with AppStudio by opening it and doing a 'Save As' elsewhere, to create a fresh copy. If you do this, several steps below can be skipped - follow the instructions)
3. Enter 'Weather App' into description in Project Properties.
4. In Project Properties, go to the Electron section and open package.json. Modify the 'dependancies' line as follows: (Skip this step if you're using the sample).
This includes the Weather-js Node library from npm.
5. To add your own icon, follow these steps. (Skip this step if you're using the sample).
- Put an png file at least 512x512 in your project directory.
- Set PhoneGap icon(1024) to that icon in Project Properties.
Add the Weather Code
1. Add a button to Form1.
2. In the Code Window for Form1, paste the following code. You'll notice there is a new function called 'require' in the first line. This function is part of Node.js: it loads the module of that name.
Since this function is not part of JavaScript, the project will not run in the browser as a normal project would.
Run the App
Now we're ready to run the app. On the Run menu, choose 'Run Desktop App using Electron'
Some notes
- The Chrome Dev Tools window opens by default. We'll need this if we are going to debug the app.
- To turn off the Chrome Dev Tools, set 'Chrome Dev Tools' to false in Project Properties.
- The 'Electron Security Warning' in the console can be ignored.
App Studio For Macbook
Distributing the App
We now have a running app. The next step is to package it for distribution. We can make regular executables for distribution on MacOS, Windows and Linux. The packaging has to done on a computer running the OS we are targeting: the MacOS version needs to be build on a Mac, etc.
There is more documentation on packaging at https://www.electron.build/. You'll need to pay special attention to code signing requirements.
On the Run menu, choose 'Make Desktop App for Distribution using Electron'. If the build fails, look at the log in 'About AppStudio' for more information.
When the build is complete, you will find the executable in your project folder, in
electron/ElectronWeather/dist/*
Tips
App Studio For Mac Os
Setting Electron Runtime Options
The operation of Electron apps at runtime can be changed by modifying the electronMain.js module. It's in the Electron section of Project Properties.
You can learn more about the options in ElectronMain.js.
How to tell if you are running Electron at runtime
How to tell if you are running Windows or MacOS at runtime
Debugging
- Check the AppStudio Log in 'About AppStudio'. It will have more info.
- To reset the Electron environment, simply delete the electron folder in your project. It will be recreated next time you start your app.
- To start your Electron app in a console, open it in the electron folder of your project directory and enter:
- To build your Electron distributable in a console, open it in the electron folder of your project directory and enter: